Ever wonder why your lights flicker or suddenly go out, and you hear that loud bang from the transformer outside? It’s frustrating and honestly a little scary, especially when you have no idea what just happened or whether it could happen again. You might be asking yourself, Why does a transformer blow? and wishing there was a clear answer that made sense without all the confusing technical jargon.
In this blog post, we’ll break down exactly why transformers fail and what causes them to blow. You’ll get simple explanations for electrical issues, overloads, insulation problems, and even weather-related causes. By the end, you’ll understand the warning signs to watch for and learn practical tips to prevent transformer problems so you can stay safe and keep your power running smoothly.
What Causes a Transformer to Blow?

Transformers are built to handle electrical loads, but exceeding their design limits can trigger catastrophic failures. Most failures fall into three categories: electrical, mechanical, and environmental. Recognizing these early can prevent damage and downtime.
- Electrical Failures: Overvoltage, short circuits, harmonics, and prolonged overload stress the windings and insulation.
- Mechanical Failures: Loose windings, tank rupture, or vibration-induced damage can physically compromise the transformer.
- Environmental Factors: Lightning strikes, flooding, strong winds, and extreme temperatures can intensify underlying weaknesses.
Mechanical vs Electrical Failures
Electrical Failures
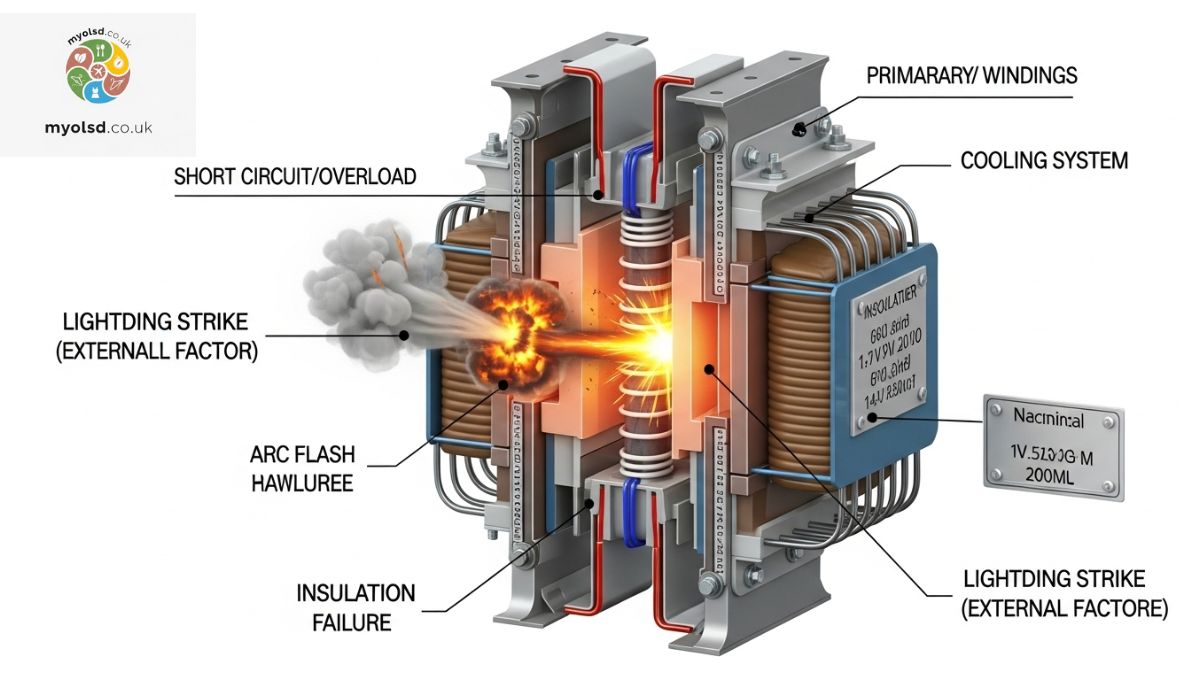
Electrical failures often start quietly but escalate rapidly. Overvoltage from lightning strikes or sudden grid surges can break down insulation, creating arcs that damage windings. Harmonics and transients from motors or industrial equipment heat the core unevenly, weakening insulation further. Overloading and inrush current at startup can produce immediate thermal stress.
Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failures involve physical stresses. Conductor tipping, hoop buckling, loose connections, oil sloshing, or poor installation can compromise integrity. Often, electrical stress triggers secondary mechanical damage. If unchecked, this leads to catastrophic transformer blowouts, posing fire and safety hazards.
Top 6 Root Causes of Transformer Blowouts

- Overvoltage Stress: Lightning, grid switching, and solar inverters can exceed the transformer’s dielectric strength, causing insulation breakdown.
- Harmonics & Load Imbalance: High total harmonic distortion and unbalanced phases create heat, straining the core.
- Inrush Current During Startup: Transformers draw 8 to 12 times rated current initially. Without mitigation, windings can arc and insulation melts.
- Thermal Overload: Faulty cooling systems or obstructed airflow cause localized overheating, carbonizing oil and weakening insulation.
- Insulation Aging or Moisture Ingress: Humidity, chemical contamination, or aging accelerates insulation failure.
- Poor Installation Practices: Loose terminals, improperly grounded bushings, or weak supports create flashover points.
Why Do Transformers Blow Up Under Load?
High load alone doesn’t destroy a transformer. Instead, prolonged stress or sudden spikes trigger failure:
- Steady Overload: Causes insulation fatigue over time
- Sudden Peak Load: Can rupture the tank or windings
- Localized Hotspots: In uncooled cores, heat exceeds 180°C, initiating arcs
Even dry-type transformers risk internal arcing if the magnetic core expands unevenly. Blowouts often occur without warning, especially under heavy or fluctuating load conditions.
Read more Article: Why Does My Toilet Whistle When I Flush It?
How Do Transformers Blow Internally?
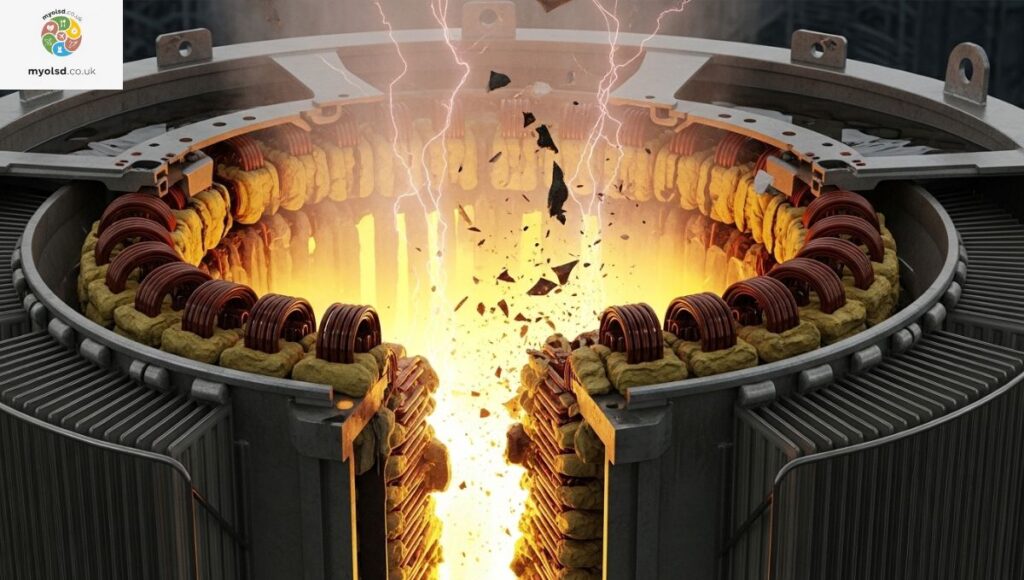

Internal transformer failure is rapid and destructive. The sequence is typically:
- Insulation fails – moisture, aging, or heat reduces dielectric strength
- Arc flashes – electricity jumps between conductors
- Arc forms plasma – extreme energy causes rapid heating
- Internal gas builds pressure – tank or casing is stressed
- Pressure ruptures casing – oil or resin may ignite
- Explosion occurs – flash, noise, smoke, and fire hazards
This chain explains why transformer failures are both sudden and dangerous, often affecting nearby equipment and personnel.
Why Do Transformers Blow During Startup or Energization?
Energizing a transformer when it’s cold introduces inrush current, which is much higher than normal operation. This causes:
- Core saturation
- Voltage spikes
- Windings to vibrate
- Instant arcs
Without soft-start systems or pre-charge logic, transformers can fail on day one. Startup is the most vulnerable phase for low- and high-voltage transformers.
What Makes a Transformer Blow in Outdoor Conditions?
Outdoor transformers face unique stressors, including:
| Environmental Factor | Impact | Preventive Measures |
| High Humidity & Rain | Speeds up insulation breakdown | IP-rated enclosures, moisture-absorbing breathers |
| Dust Accumulation | Partial discharge & flashover | Protective grills, periodic cleaning |
| UV Exposure | Weakens insulation coating | UV-stable resin, tropicalization |
| Rodent Intrusion | Wire damage | Rodent-proof grills |
| Poor Ventilation | Overheating | Fin-type cooling, proper airflow |
Transformers with these protections are less likely to blow even under adverse weather conditions.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs of Transformer Failure
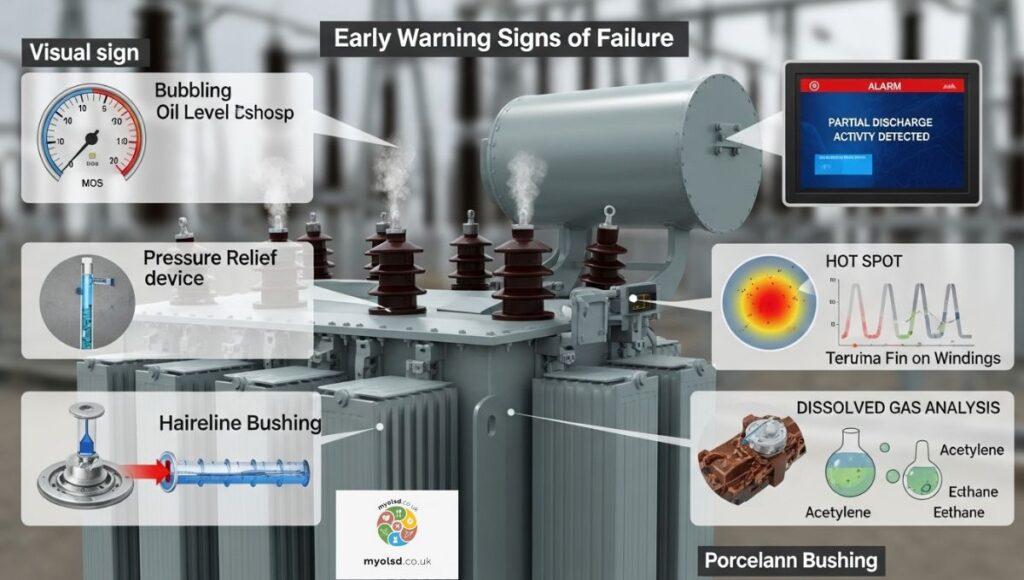
Physical & Audible Indicators
- Unusual humming or buzzing
- Flickering lights or temporary power dips
- Smoke, sparks, or smell of burning oil
- Oil leaks or discoloration
Monitoring for Internal Stress
- Hydrogen Monitoring: Hydrogen is released first during insulation breakdown
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detects overheating and electrical stress in oil
- Partial Discharge Monitoring: Identifies insulation weakness before failure
- Temperature & Vibration Analysis: Tracks abnormal heat and mechanical stress
Early detection allows preventive measures before catastrophic blowouts.
What Happens During a Transformer Blow?
When a transformer fails:
- Noise & Physical Damage: Loud bang, vibrations, broken bushings
- Fire & Explosion Risk: Ignited insulation oil or resin
- Electrical Hazards: Short circuits, voltage spikes, and arcs
- Power Outages: Can disrupt local grids or industrial operations
- Emergency Response Activation: Firefighters, repair crews, and utility workers respond
Blowouts can damage nearby equipment and endanger personnel. Professional inspection and repair are essential.
How to Handle a Transformer Explosion
Immediate safety steps:
- Isolate the transformer from all power sources
- Activate emergency response protocols
- Secure the area with hazard signage
- Notify utility and emergency teams
- Avoid touching equipment or downed lines
- Use flashlights, not candles, during outages
- Wait for certified personnel to restore power
Quick action prevents injury, further damage, and legal liabilities.
Maintenance and Prevention Best Practices

Preventing transformer blowouts requires proactive care:
- Inspect monthly for leaks, heat, or unusual noises
- Monitor oil levels, cooling systems, and bushings
- Test alarms, fuses, and protection devices quarterly
- Conduct annual inspections with DGA and vibration analysis
- Perform winding resistance and oil quality checks every 3 to 5 years
Certified transformers with patented safety features, like Linkwell or Shinenergy units, reduce the risk of fire, explosion, and electrical hazards.
High-Voltage vs Low-Voltage Transformer Risks
High-voltage transformers face larger surge risks, insulation stress, and more dramatic explosions. Low-voltage transformers are safer, especially if equipped with protective devices and monitoring systems. Choosing quality, certified equipment is crucial for industrial, commercial, or residential installations.
Summary: Predict, Prevent, and Protect
Transformers blow because of electrical stress, insulation failure, mechanical stress, environmental damage, or a combination of factors. Regular inspection, predictive maintenance, monitoring, surge protection, and emergency preparedness dramatically reduce risks. Certified, high-quality transformers ensure operational safety, prevent injuries, and avoid costly downtime.
Key Takeaways:
- Electrical faults, mechanical stress, and environmental hazards are leading causes
- Early warning signs include noise, heat, smoke, flickering lights, and oil leaks
- Preventive maintenance and monitoring prevent most transformer explosions
- Certified units with patented safety technology minimize fire, property, and personal damage
- Immediate emergency response is essential for blown transformers
FAQs
How long does it take if a transformer blows?
The duration to fix a blown transformer depends on the damage, availability of spare parts, and complexity. Repairs can take anywhere from a few hours for minor issues to several days for severe damage.
What to do if you hear a transformer blow?
Immediately stay away from the area, avoid touching electrical equipment, and call the power company or emergency services. Ensure others are safe until professionals arrive.
Why do transformers blow in the winter?
Cold weather can thicken insulation oil and make materials brittle, increasing stress during energization. Sudden demand spikes and ice-related damage also contribute.
How common are transformer explosions?
Transformer explosions are rare, especially with modern, properly maintained units. Most failures are minor or preventable with regular inspection and surge protection.
What happens if a transformer blew?
A blown transformer can cause power outages, fire risks, electrical hazards, and damage to connected equipment. It may also release smoke or oil, requiring emergency response.
How can transformer explosions be prevented?
Regular maintenance, predictive monitoring, proper load management, surge protection, and certified equipment with safety features significantly reduce explosion risk.
Why would a transformer keep blowing?
Repeated blowouts often indicate underlying issues like overloading, insulation deterioration, faulty connections, or persistent voltage surges. Professional inspection is necessary.
How much damage can a transformer explosion cause?
Explosions can damage the transformer, nearby equipment, property, and infrastructure. They can also pose serious safety risks, including fires and injuries.
What causes transformer fires?
Fires are usually caused by insulation failure, oil leaks, electrical arcing, overloading, or exposure to external hazards like lightning or debris impact.
How much does it cost to replace a transformer?
Costs vary by type, size, and voltage. Low-voltage units may cost a few hundred dollars, while large industrial or high-voltage transformers can run into tens of thousands of dollars.
How long do transformers usually last?
With proper maintenance, most transformers last 20 to 30 years. Factors like load stress, environmental conditions, and oil quality can affect lifespan.

1 thought on “Why Does a Transformer Blow? Understanding Causes, Risks, and Prevention”